Different SQL Joins Explained
Databases
27/05/2021
In a previous blog post, I covered the basics of an SQL JOIN statement. I'd like to further elaborate on the 4 different types of Joins that exist.
The Venn diagrams below give a great overview of how they work, which I recommend you use as a reference to my explanations below.
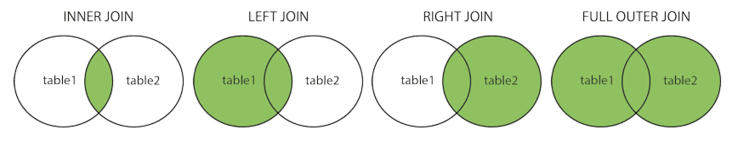
Sourced from W3Schools
I will also reuse from my previous post the -
Pets and
| Id | Age | Name |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 12 | Sandy |
| 2 | 7 | Odie |
Owners tables to illustrate each JOIN statement.
| Id | Name | Pet_Id |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Dilshan | 2 |
| 2 | John | NULL |
Be aware that not every SQL database supports a RIGHT JOIN and FULL OUTER JOIN.
INNER JOIN
Executing a JOIN statement without specifying the type will always default to an INNER JOIN. This type will only return rows that have matching values (i.e. pet IDs) in both tables.
SELECT * FROM Pets JOIN Owners ON Pets.Id=Owners.Pet_Id;Query output:
| Id | Age | Name | Id | Name | Pet_Id |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 7 | Odie | 1 | Dilshan | 2 |
LEFT JOIN
In a LEFT JOIN, the entire left-hand table is included even if a row doesn't have a match. Consequently, NULL values are used on the right-hand side to represent this missing match.
SELECT * FROM Pets LEFT JOIN Owners ON Pets.Id=Owners.Pet_Id;Query output:
| Id | Age | Name | Id | Name | Pet_Id |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 12 | Sandy | NULL | NULL | NULL |
| 2 | 7 | Odie | 1 | Dilshan | 2 |
RIGHT JOIN
A RIGHT JOIN is identical to a LEFT JOIN, but only reversed. That means the entire right-hand table is included along with matching (empty) rows on the left-hand side.
SELECT * FROM Pets RIGHT JOIN Owners ON Pets.Id=Owners.Pet_Id;Query output:
| Id | Age | Name | Id | Name | Pet_Id |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 7 | Odie | 1 | Dilshan | 2 |
| NULL | NULL | NULL | 2 | John | NULL |
FULL OUTER JOIN
A FULL OUTER JOIN, or simply OUTER JOIN, is basically a combination of the previous two. Here, all the records on both tables are included along with empty rows for any missing matches.
SELECT * FROM Pets OUTER JOIN Owners ON Pets.Id=Owners.Pet_Id;Query output:
| Id | Age | Name | Id | Name | Pet_Id |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 12 | Sandy | NULL | NULL | NULL |
| 2 | 7 | Odie | 1 | Dilshan | 2 |
| NULL | NULL | NULL | 2 | John | NULL |
